[컴퓨터구조] #11. Single-Cycle MIPS(2)
Lec 11. Single-Cycle MIPS_2 (The Processor)
* Micro-architecture의 구성요소 (lec10 참고)
- Datapath (ALU)
- Control (Control Unit)
-> (lec11)에서는 design control logic !
- lw


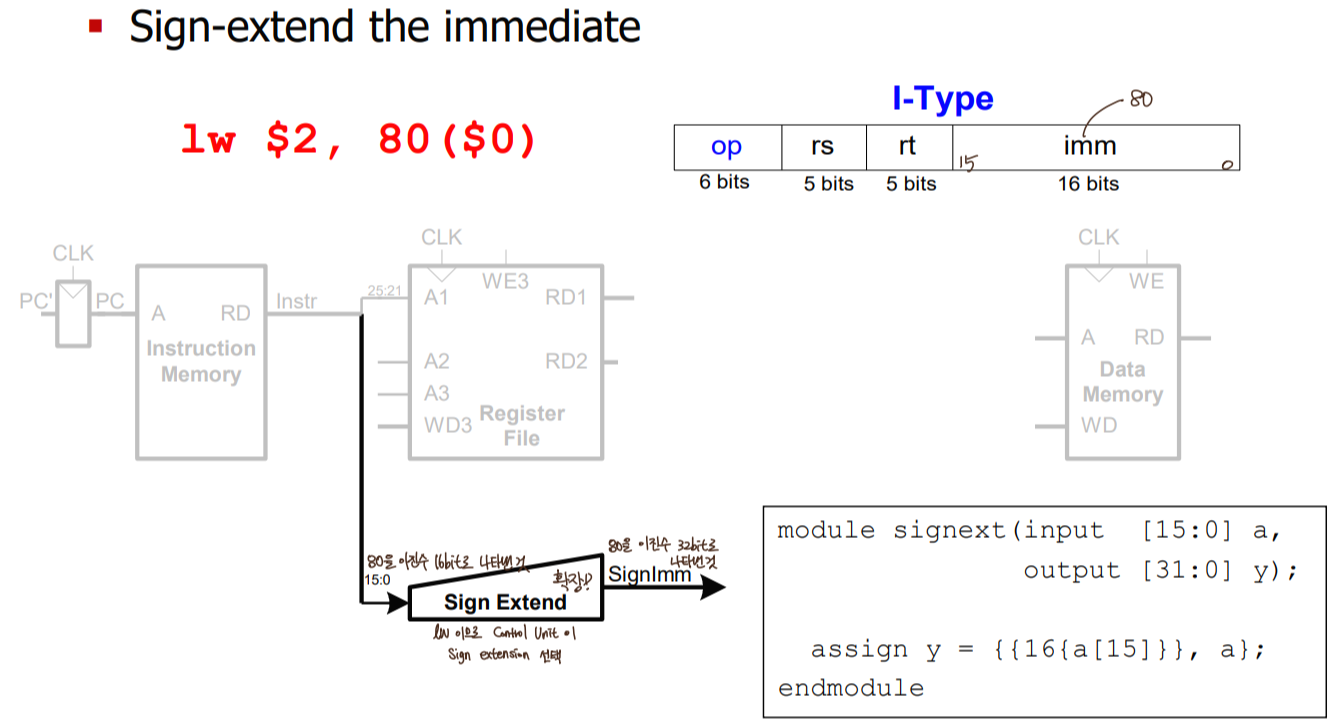


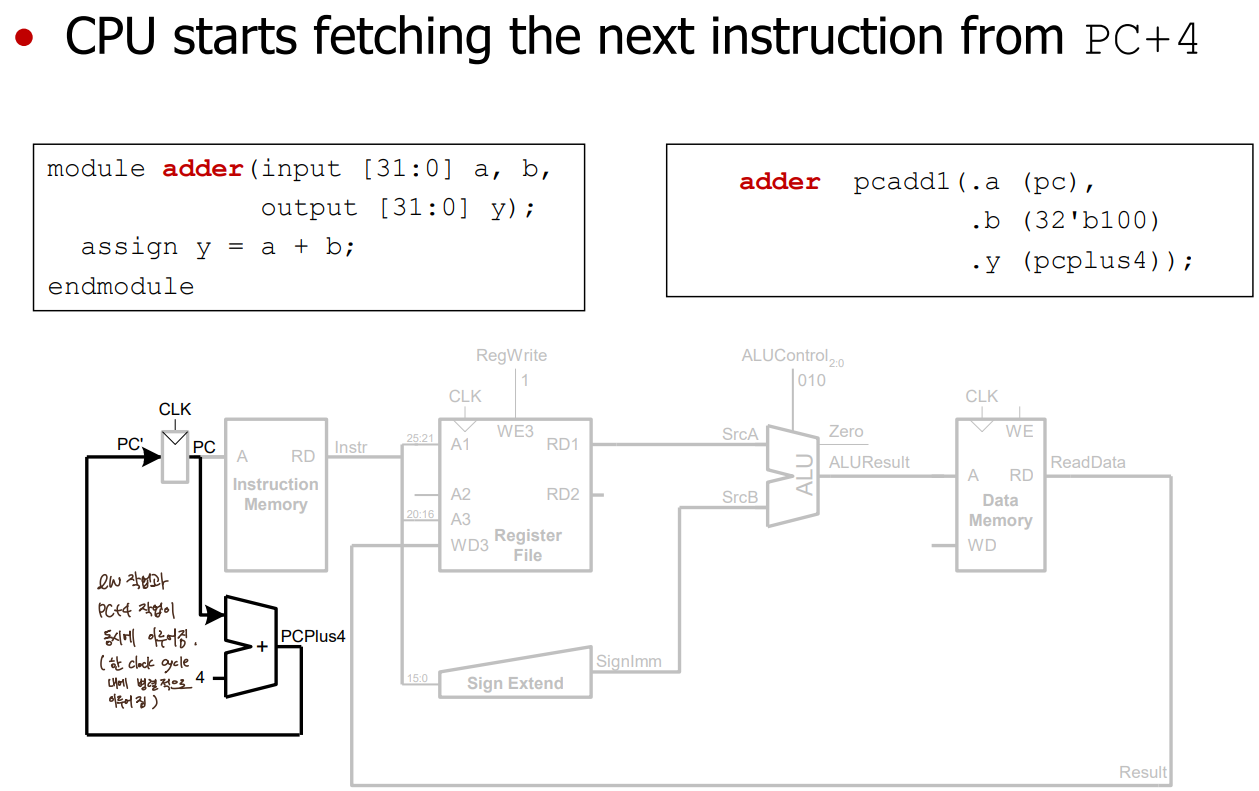
- pc
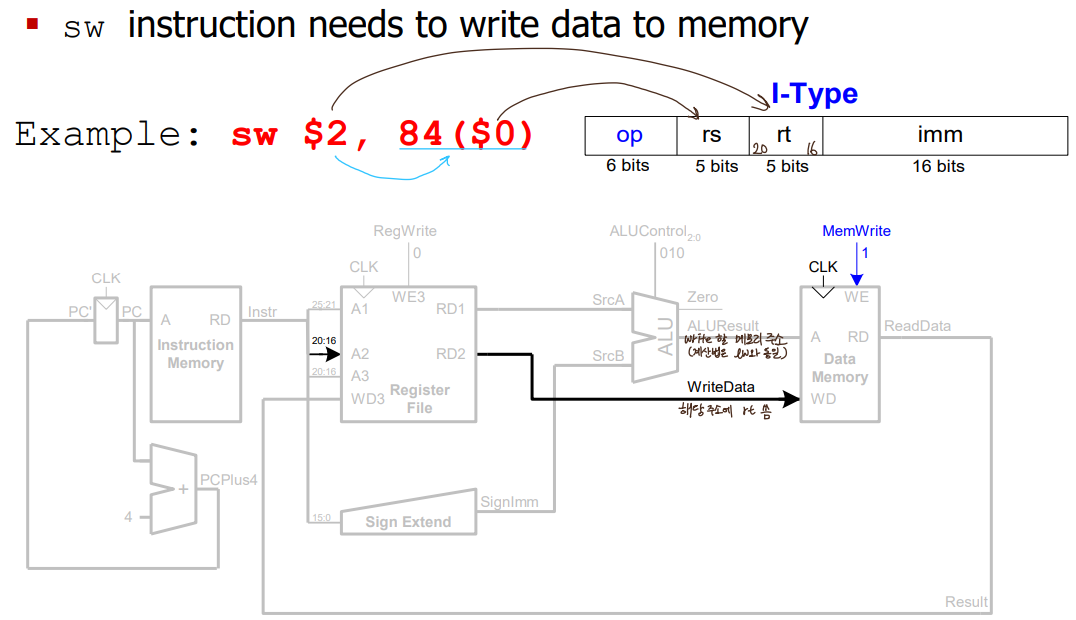
- sw
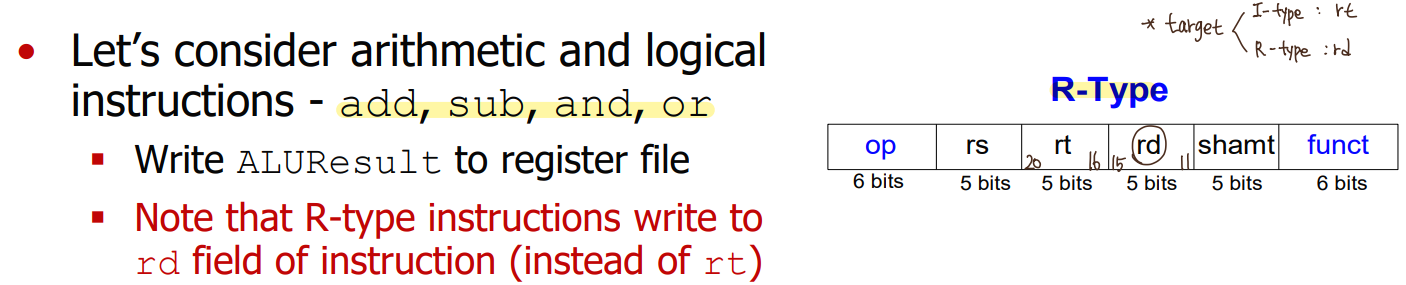
- add, sub, and, or
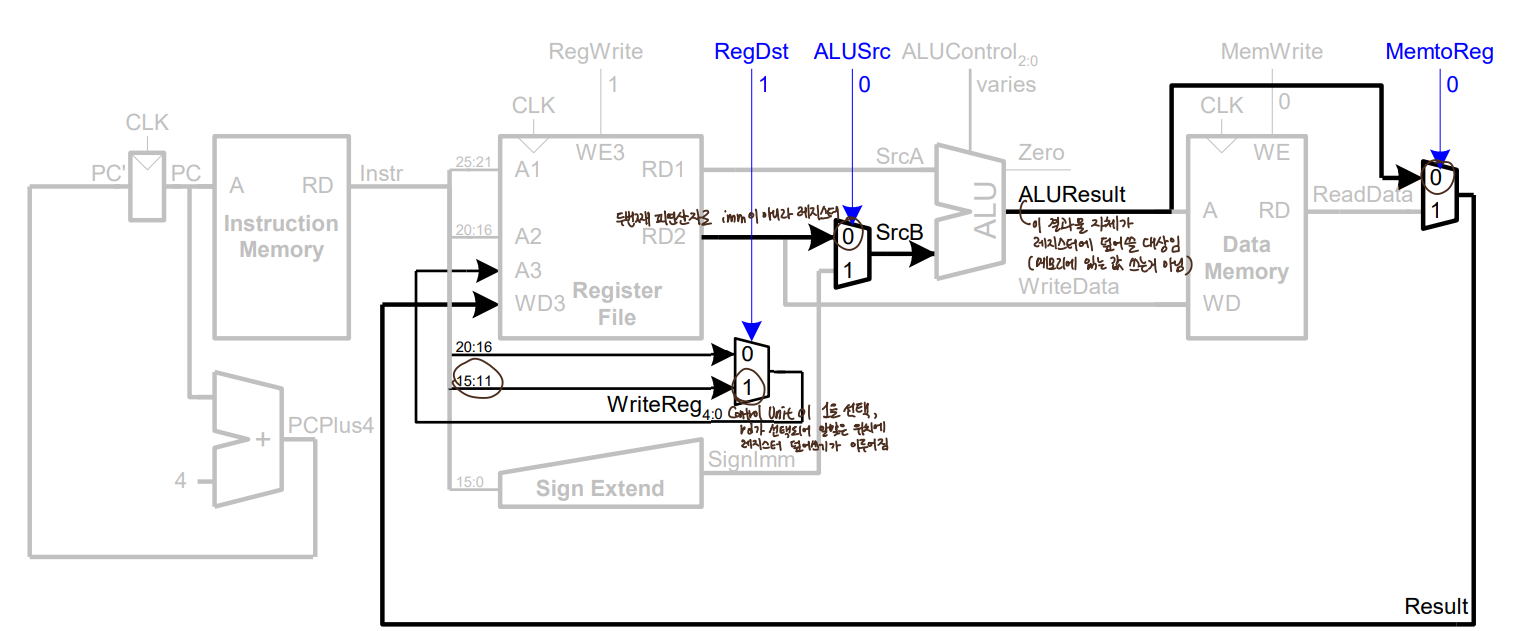
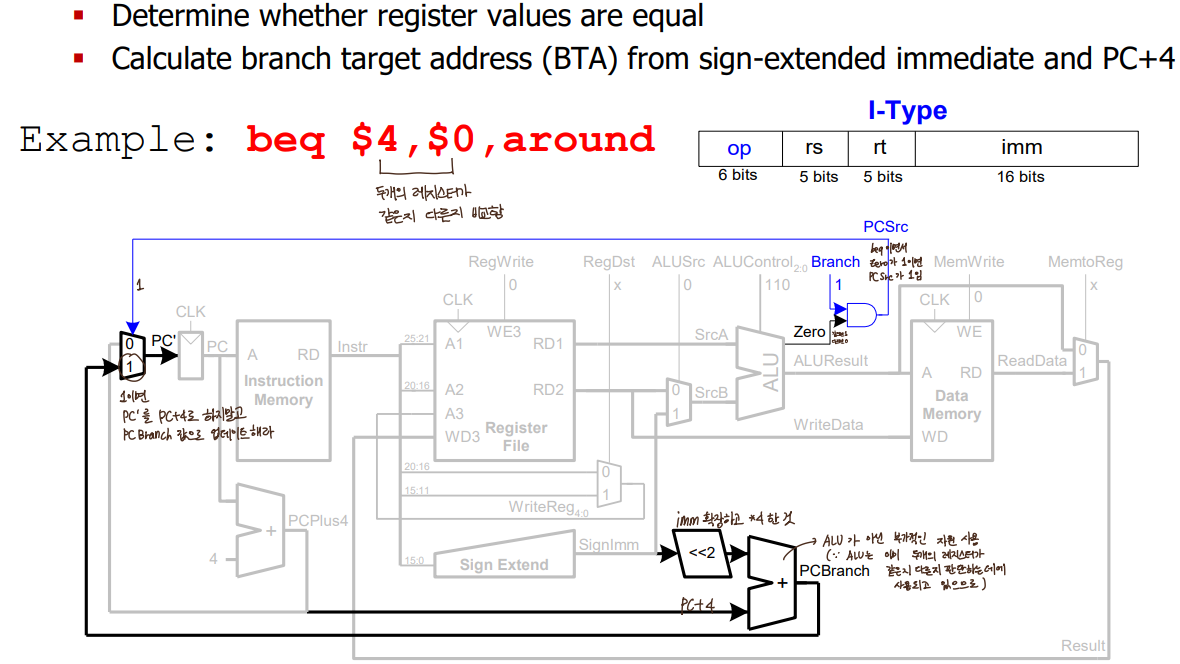
- beq
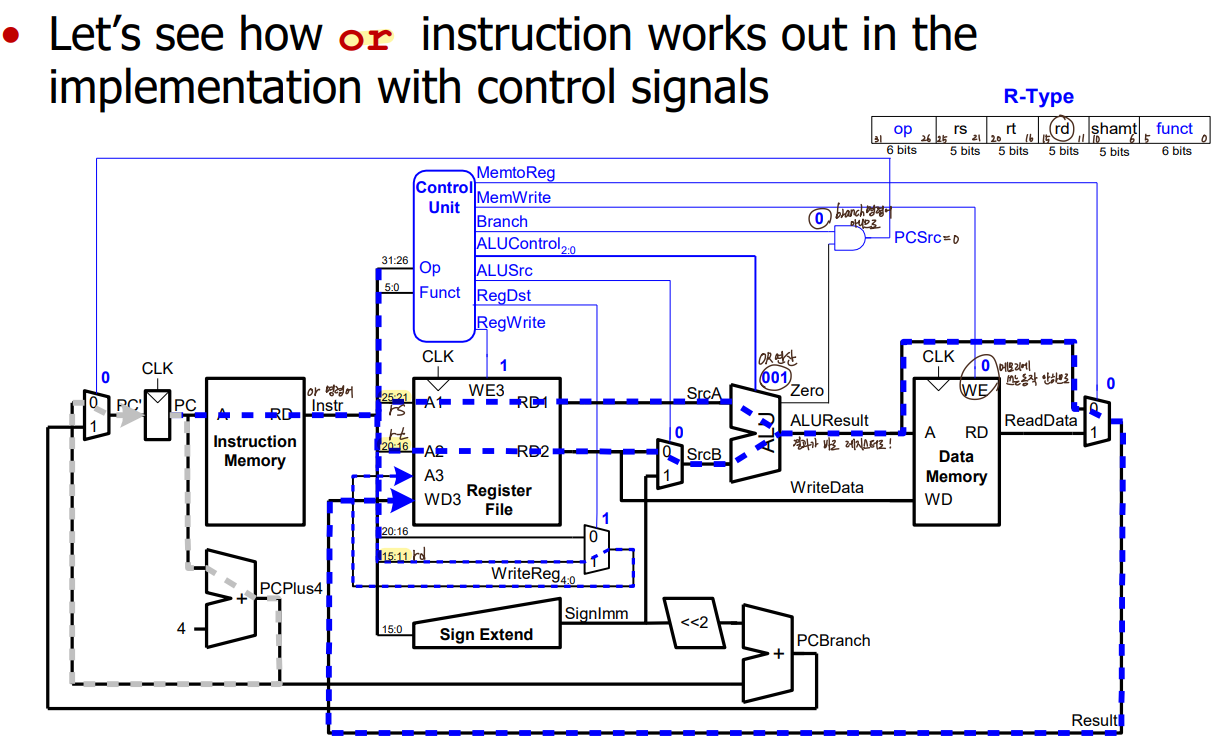
- or
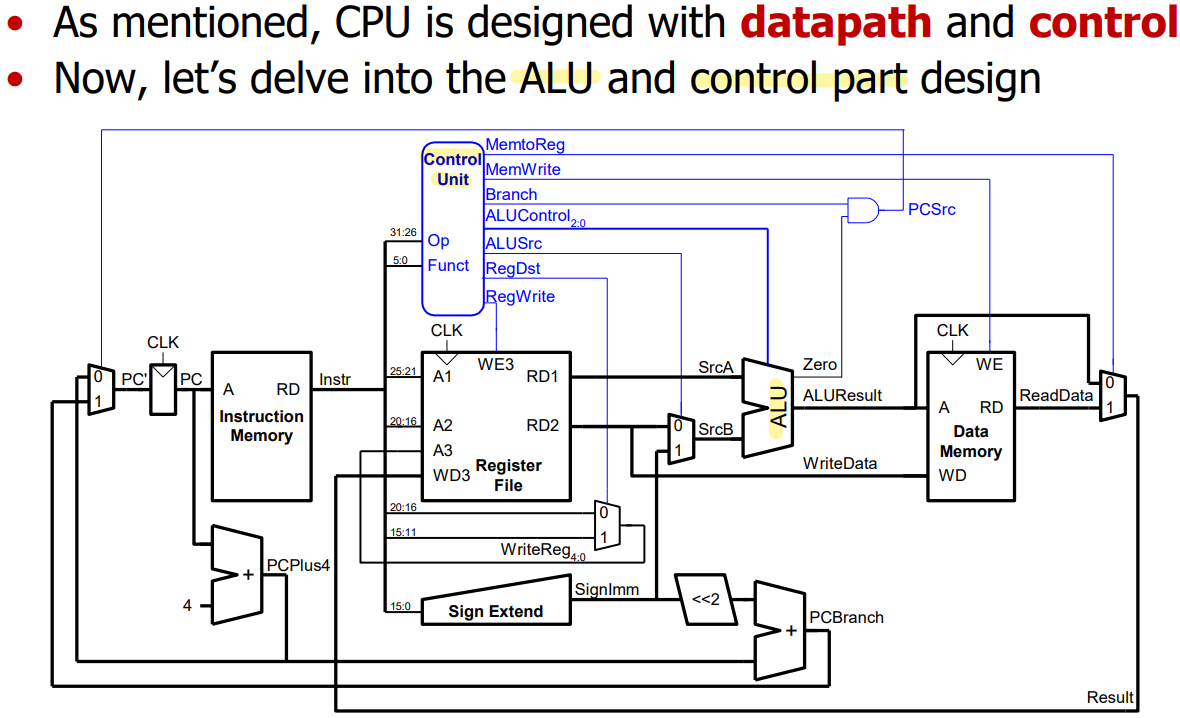
- ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)
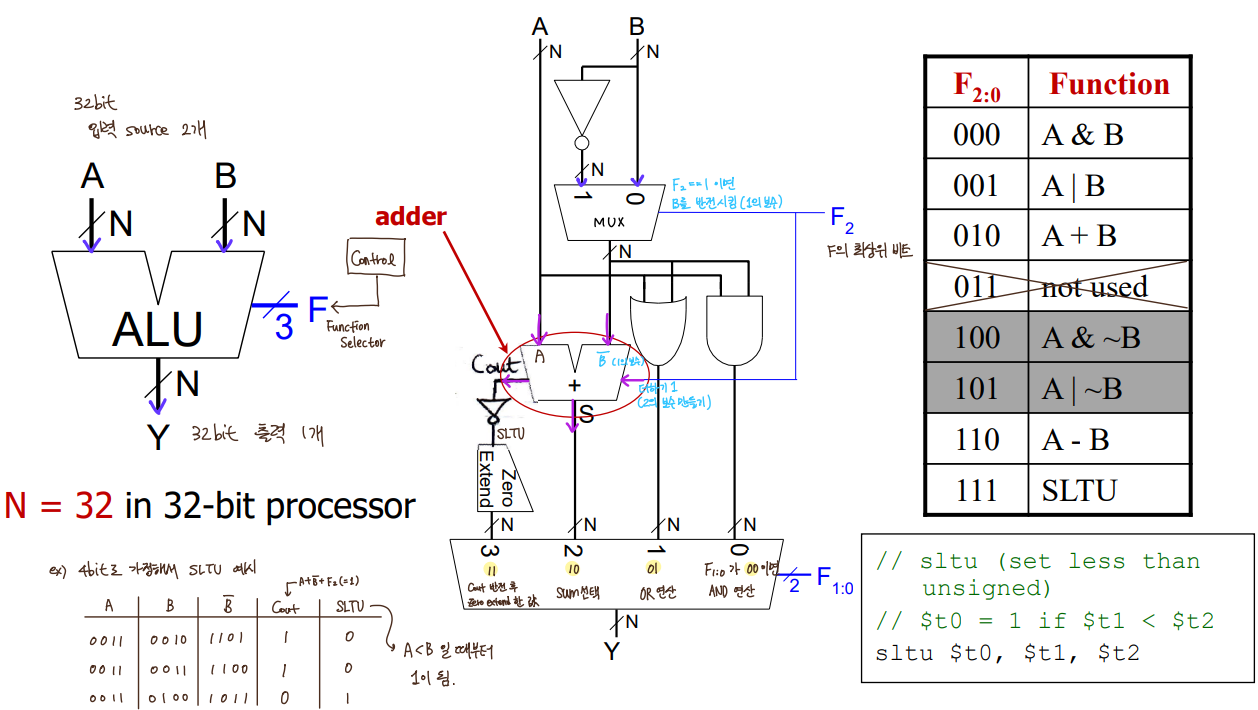
input : A, B, F
output : Y
F의 최상위 비트가 1이면 B를 1의 보수를 취함.
A + ~B + 1 의 carryout을 반전시키고 zero extend한 값이 SLTU임.
A<B 일때부터 SLTU 값이 1이 됨.
- Verilog Code _ ALU
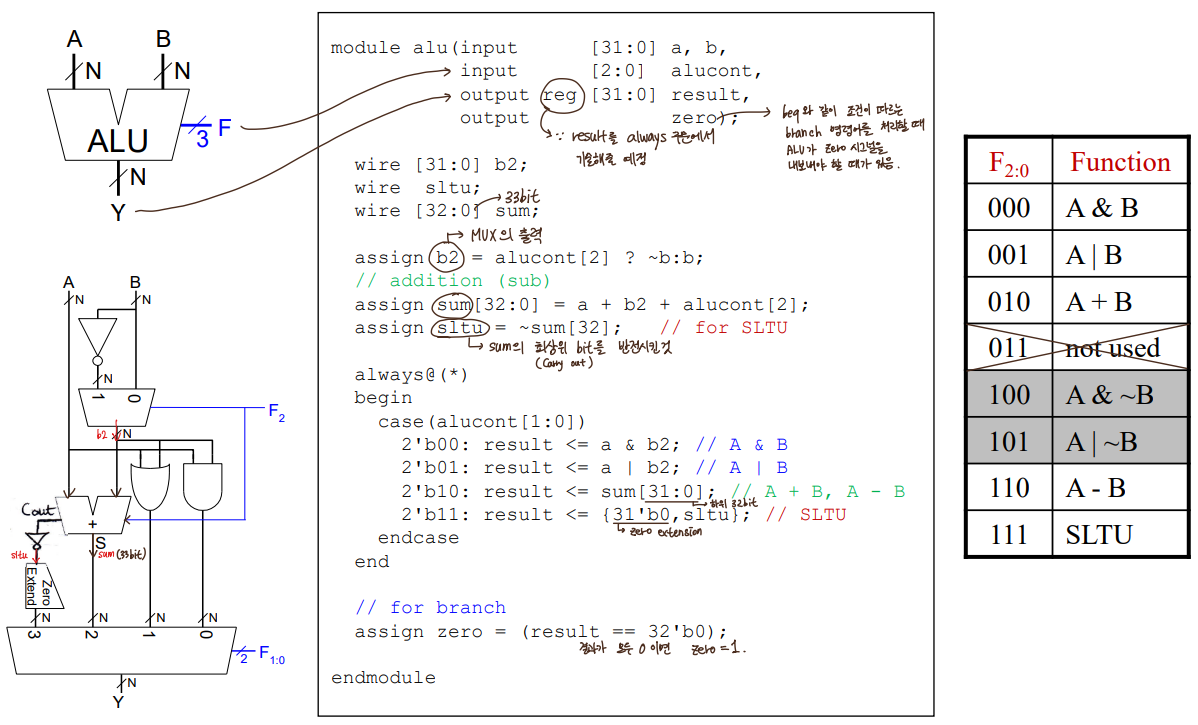
input : A(a), B(b), F(alucont)
output : Y(result), (zero)
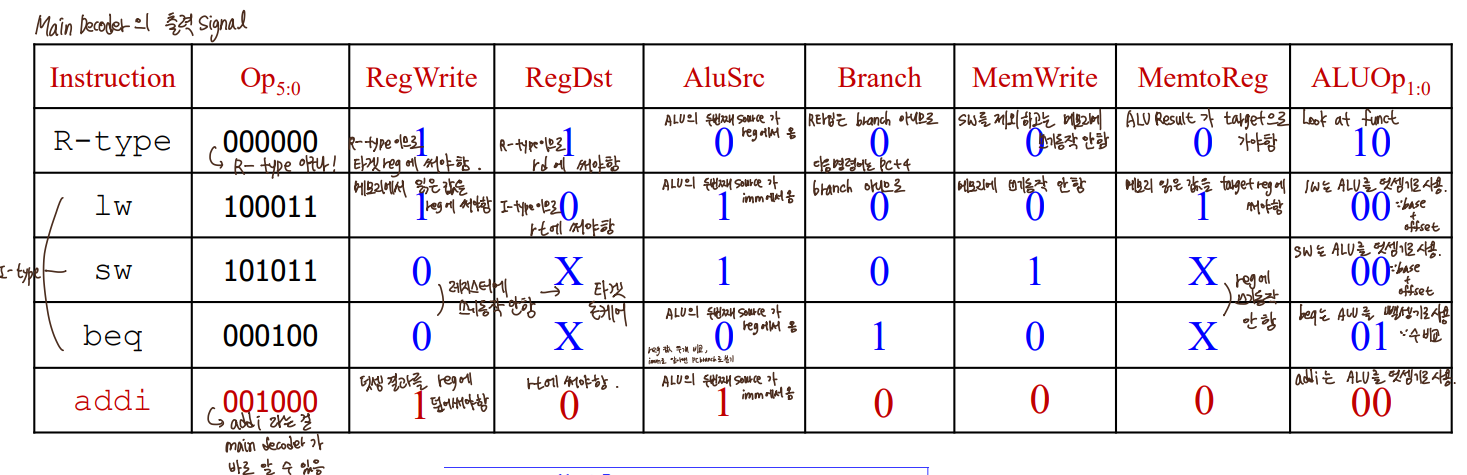
- Control Unit

명령어 fetch해서 Opcode와 Funct를 알아냄
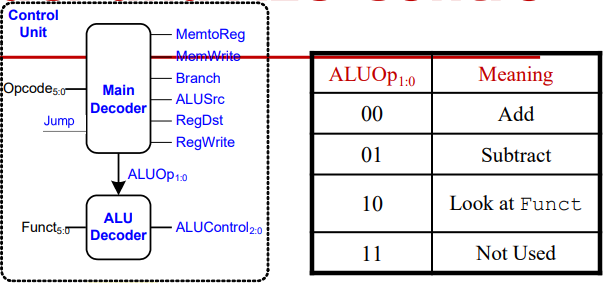
-> Main Decoder가 Opcode를 보고 ALUOp를 ALU Decoder에게 전달, data path에게 6가지 제어신호 전달
-> ALU Decoder는 data path에게 ALUControl 전달.
- Control Unit _ ALU Control
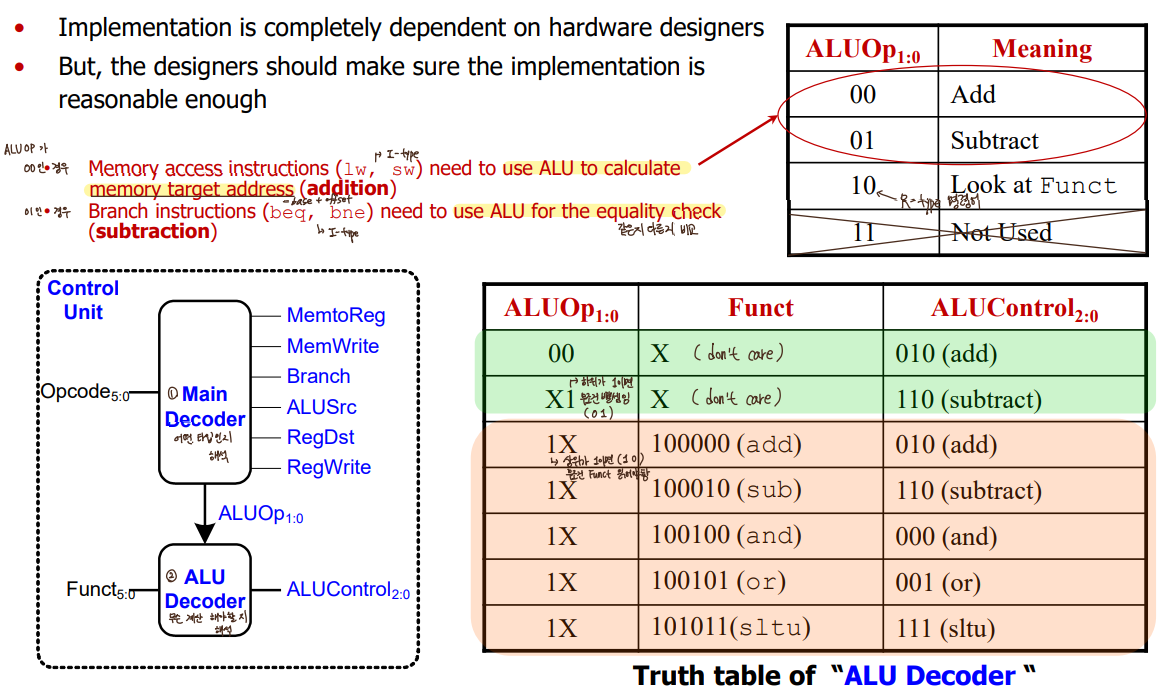
I-type은 Opcode만 보고 명령어 뭔지 알 수 있음 -> lw,sw이면 00, beq,bne이면 01을 ALUOp로 전달
R-type은 Opcode만 보고 무슨 명령어인지 모름, Funct도 봐야함 -> 10을 ALUOp로 전달(Look at Funct)
- Control Unit _ Main Decoder
R-type, lw, sw, beq

addi
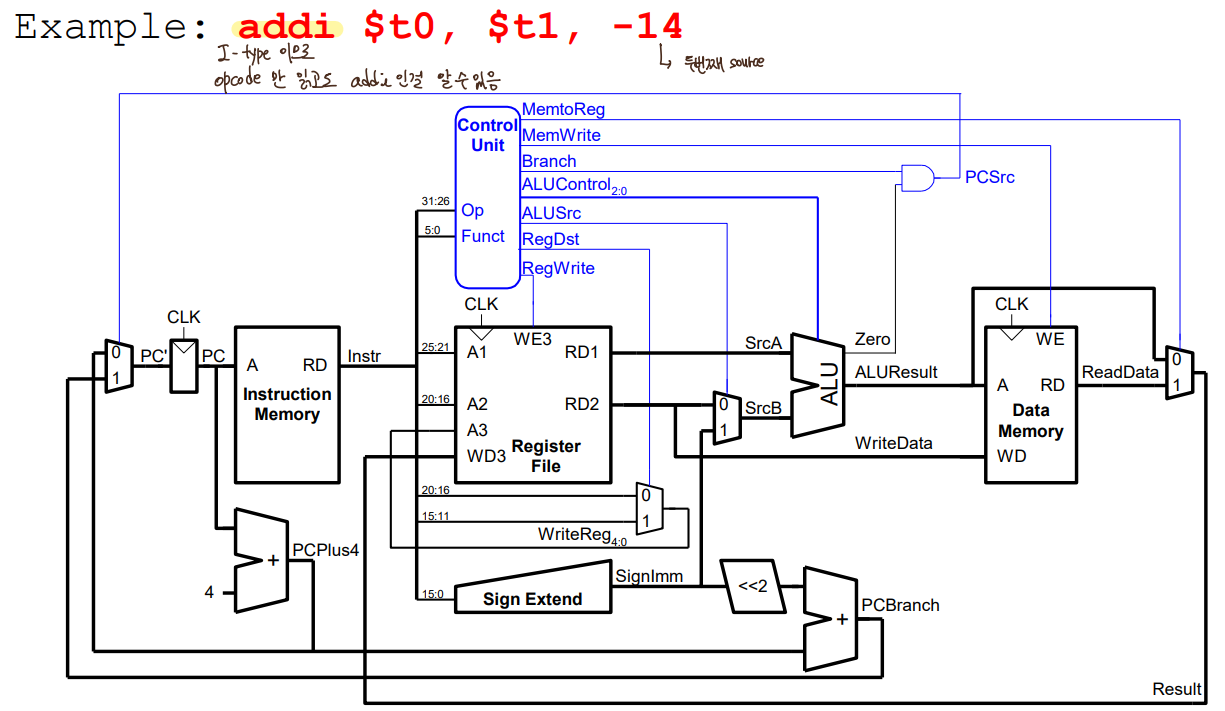
j
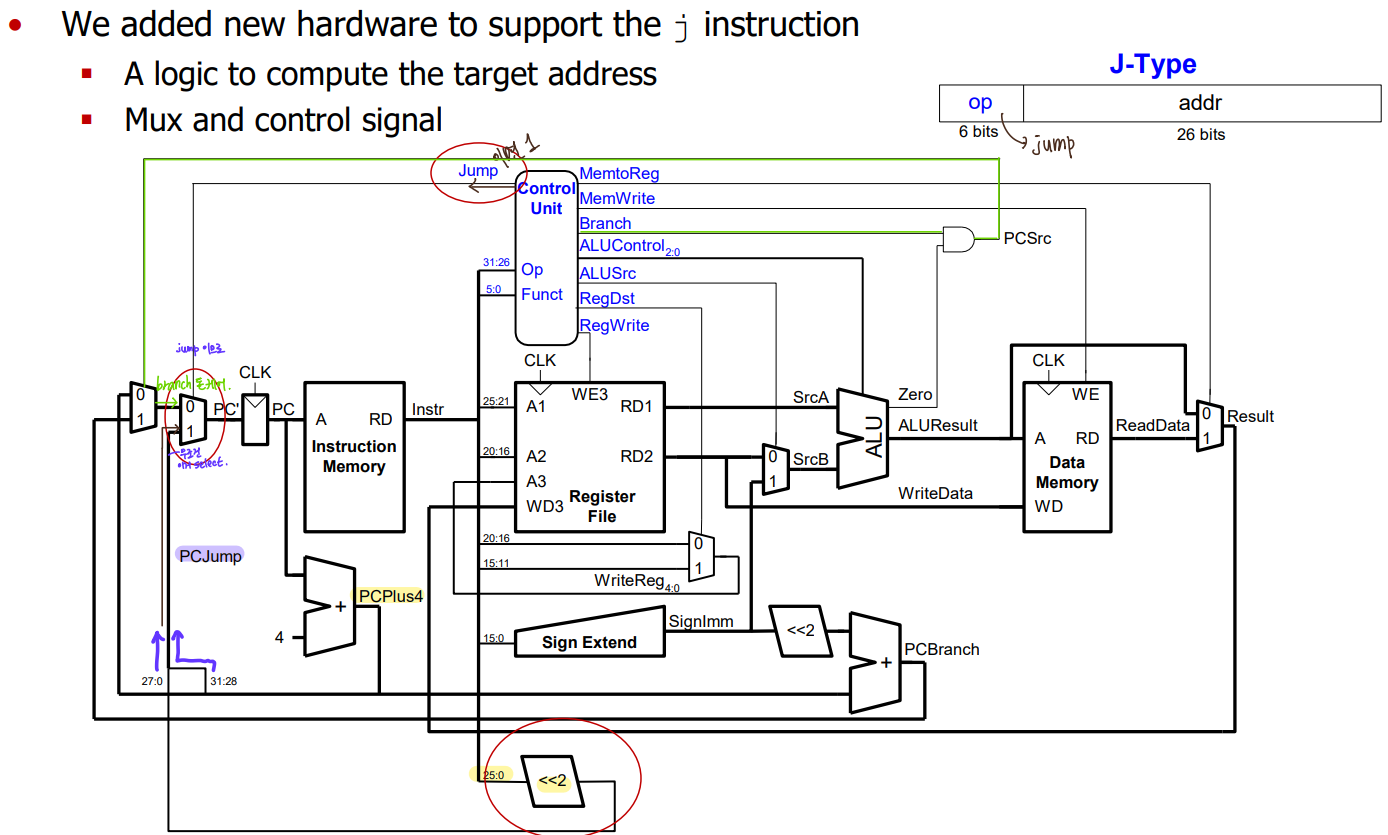
destination = {PC+4의 상위 4bit, addr <<2}
-> PC+4가 포함되어있는 임의의 256MB 안에 아디로든 점프 가능(lec6 참고)

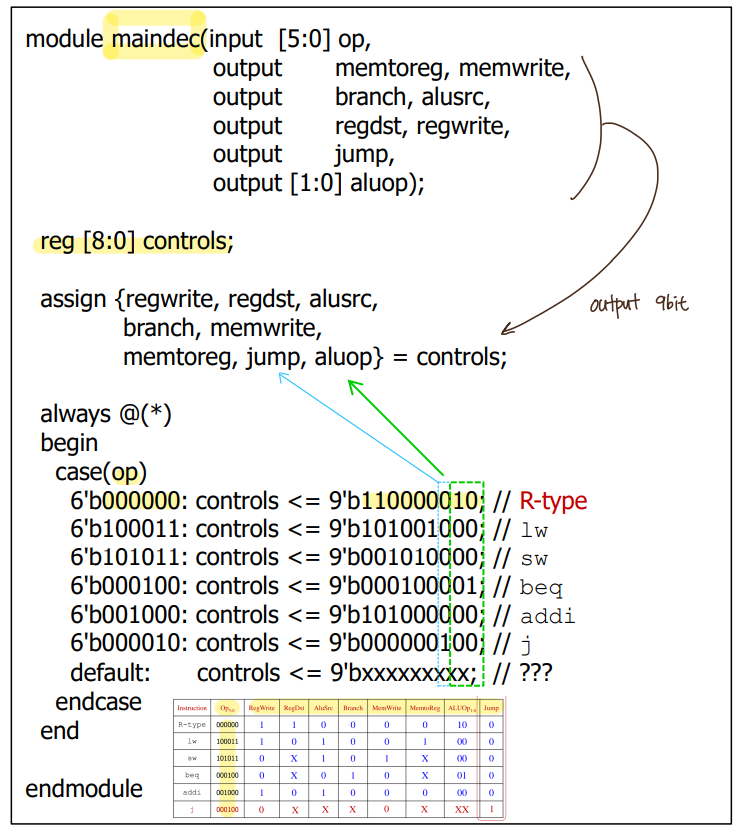
- Verilog Code _ Main Decoder and ALU Control

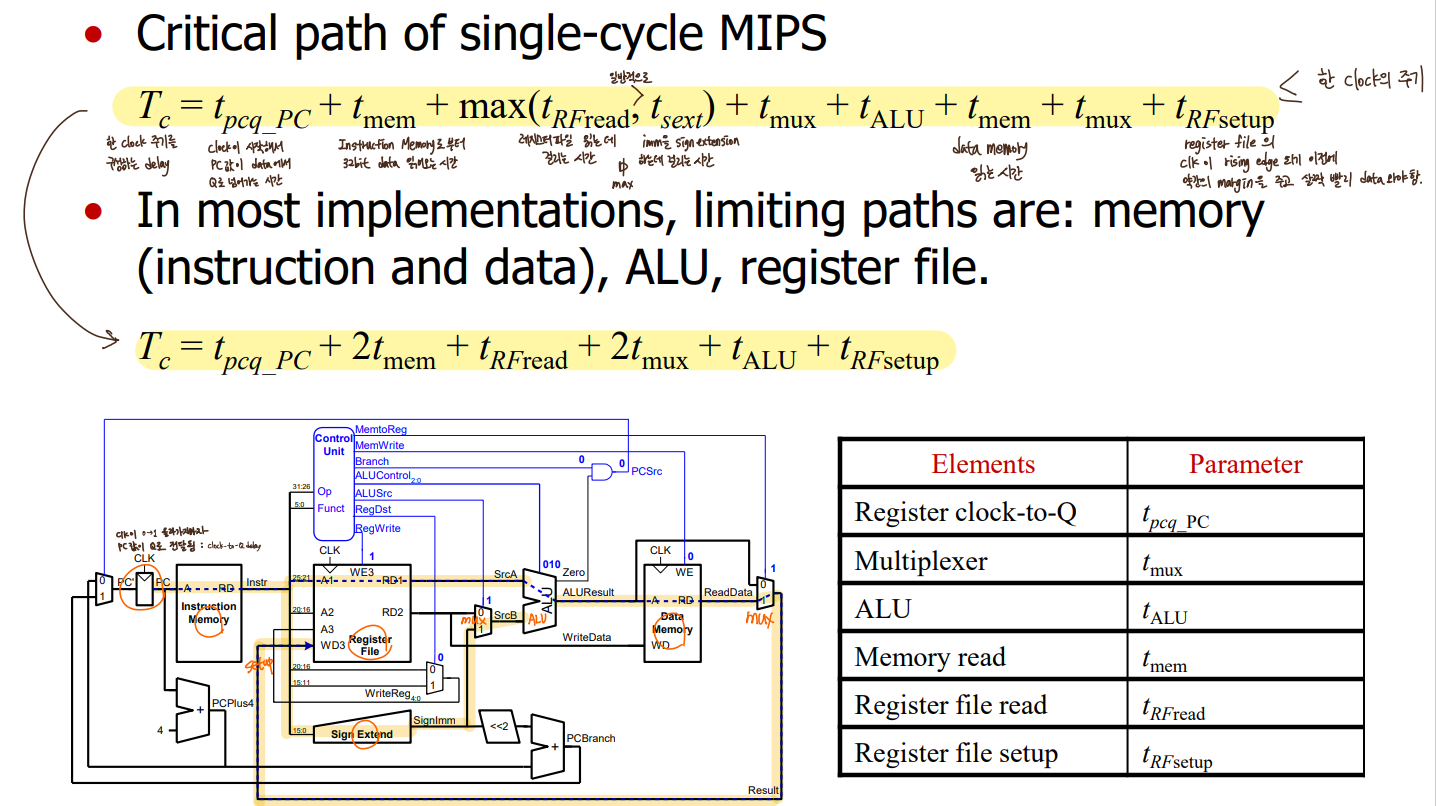
- Single-Cycle MIPS Performance

가장 오래 걸리는 경로가 critical path임.
add, sw, lw중에서는 lw가 critical path.
critical path가 짧을수록 performance 좋아짐.
- Example

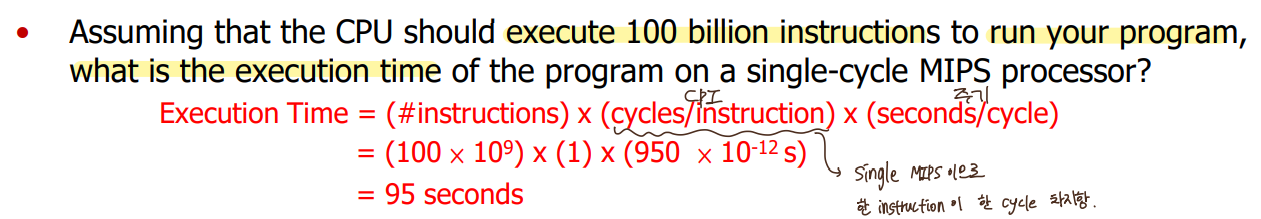
* CPU Time (lec8 참고)
= # insts * CPI * T
= # insts * CPI / f